Introduction to Sole Proprietorship Firms
The term "sole" in sole proprietorship refers to the fact that there is a single owner who takes on all the risks and rewards of the business. "Proprietorship" emphasizes the ownership aspect, indicating that the business is owned and operated by one person.
A sole proprietorship is a form of business organization where an individual runs and manages a business on their own. It is the simplest and most common type of business structure, often chosen by small businesses and self-employed individuals.
In a sole proprietorship, the owner and the business are considered one and the same in the eyes of the law. This means that there is no legal distinction between the individual and the business entity. The owner retains full control over the business's operations, decision-making, and profits.
FEATURES OF SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
- Single Ownership
- No sharing of profit and loss
- One man's Capital
- Unlimited Liability
- Less Legal Formalities
- One man Control
1. Single Ownership: A sole proprietorship is owned by an individual who has complete control and authority over the business. The owner is solely responsible for making all decisions and managing the operations. And this feature itself indicated by the form of business.
2. No Sharing of Profit and loss: The owner of a sole proprietorship retains all profits generated by the business. Similarly, they are solely responsible for any losses incurred by the business.
3. One man’s capital: In a sole proprietorship, the capital used to start and operate the business typically comes from the owner's personal funds. Since the owner has complete control and ownership of the business, they are responsible for providing the necessary capital to finance the business activities.
4. Unlimited Liability: The owner has unlimited personal liability for all debts and obligations of the business. This means that the owner's personal assets can be used to satisfy business liabilities, putting their personal wealth at risk.
5. Less Legal Formalities: Compared to other business structures like corporations, sole proprietorships generally have fewer legal requirements and compliance obligations like Business registration as some jurisdictions may require sole proprietorships to register their business name or obtain necessary licenses or permits, the registration process is typically simpler and less formal compared to other business structures.
6. One Man Control: As the sole owner, the proprietor has full control over all aspects of the business, including decision-making, management, and operations. This can be an advantage for those who prefer to have autonomy and direct involvement in their business.
ADVANTAGES OF FORMING A SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP FIRM

1. Easy Formation: Establishing a sole proprietorship is relatively easy and straightforward. There are usually no complex legal requirements or extensive paperwork involved, making it a simple and quick process to start a business.
2. Quick Decision: The absence of a formal decision-making structure in sole proprietorships means that you can adapt and implement changes more rapidly. This agility can be advantageous in industries where quick decision-making and flexibility are crucial, such as in fast-paced markets or when responding to emerging trends.
3. Complete Control: As the sole owner, you have full control and decision-making authority over all aspects of the business. You can make quick decisions without the need for consultation or consensus from other owners or partners.
4. Flexibility: Sole proprietorships offer great flexibility in terms of operations, business focus, and adapting to market changes. You have the freedom to change the direction of the business, modify products or services, and adjust strategies quickly to meet evolving customer demands.
5. Cost Effective: Running a sole proprietorship can be cost-effective, as there are generally fewer startup and operational expenses. There are no costs associated with forming and maintaining a separate legal entity, such as filing fees or annual reporting fees.
6. Privacy: Unlike corporations or LLCs, sole proprietorships are not required to disclose detailed financial information or ownership details to the public. This can provide a level of privacy for the business owner.
REGISTRATION PROCESS FOR SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
Note: It's important to note that the registration process can vary depending on your jurisdiction.
The Basic Registration Process is as follow
1.Choose a business name: Select a unique name for your sole proprietorship. Ensure that the name does not infringe on any existing trademarks or business names. It is advisable to conduct a search on the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) website to check the availability of the name.
2. Obtain a PAN (Permanent Account Number): Apply for a PAN from the Income Tax Department. A PAN is a unique identification number required for tax purposes. You can apply online through the NSDL website or visit the nearest PAN facilitation center.
3. Open a bank account: Open a separate bank account for your sole proprietorship. Choose a bank that suits your requirements and provides facilities for sole proprietorships. You will need to provide your PAN and other relevant documents as per the bank's requirements.
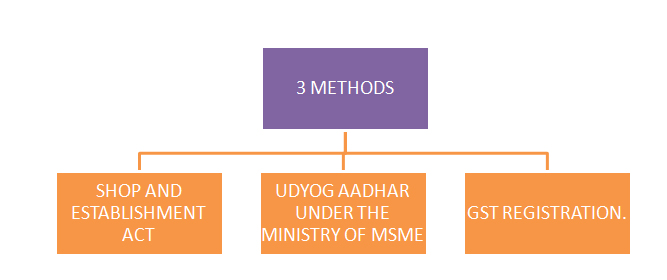
4. Register under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) (if applicable): If your annual turnover exceeds the threshold set by the government (currently INR 20 lakhs for most states), you are required to register for GST. You can register online through the GST portal by providing the necessary details and documents.
5. Register under the Shops and Establishments Act: Depending on the state you are operating in, you may need to register your sole proprietorship under the respective Shops and Establishments Act. This registration is typically done with the local Municipal Corporation or labor department. You will need to provide details about your business and premises.
6. Obtain any required licenses or permits: Depending on the nature of your business, you may need to obtain specific licenses or permits. For example, if you are involved in food-related activities, you may need to obtain a Food Safety License. Determine the licenses and permits applicable to your business and obtain them from the respective authorities.
7. Optional: Register under the Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSME) Act: If your sole proprietorship qualifies as a micro, small, or medium enterprise based on turnover or investment criteria, you may choose to register under the MSME Act. This registration can provide benefits such as access to government schemes, subsidies, and priority in certain tender processes.
8. Maintain proper books of accounts: As a sole proprietorship, it is essential to maintain accurate financial records of your business transactions. This includes recording sales, purchases, expenses, and other financial details. You may also need to periodically file income tax returns based on the applicable tax rules.
DOCUMENTS REQUIRED FOR REGISTRATION
- Aadhar Card
- Pan Card
- Bank Account
- Registered Office Proof (Rent agreement for a rented property or Electricity or utility bill for the self-owned property.)
FOLLOWING ARE SOME BASIC COMPLIANCE NEED TO BE DONE BY SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP AFTER REGISTRATION IF APPLICABE
- Income Tax Return.
- GST Return.
- Accounting and Book-Keeping.
- TDS Return.
- EPF Return.
- Tax Audit.
- Business Licenses and Permits.
- And any other compliance as applicable.
FAQ
Q.1. What is a sole proprietorship?
Ans: A sole proprietorship is a type of business structure where a single individual owns and operates the business.
Q.2. Who can opt for Sole Proprietorship?
Ans: Any person who wants to start a business with less investment can opt for this type of business form.
Q.3. How is a sole proprietorship different from other business structures?
Ans: Unlike corporations, partnerships, or limited liability companies (LLCs), a sole proprietorship does not create a separate legal entity. The owner and the business are considered one and the same, which means the owner has unlimited personal liability.
Q.4. Registration is mandatory for Sole proprietorship?
Ans: No, Sole Proprietorship Registration is not mandatory.
Q.5. What is the minimum capital needed to form a sole proprietorship firm?
Ans: There is no prescribed minimum capital for starting a sole proprietorship firm.
Q.6. Can a salaried person or a person in the employment form a sole proprietorship firm?
Ans: Yes, a salaried person or person in employment can form a sole proprietorship firm. However, one needs to check the employment agreement or terms of employment if it has certain restrictions.
Q.7. Can a minor person starts a Sole Proprietorship Firm?
Ans: No, a minor whose age is below 18 cannot start a Sole Proprietorship Firm on his own because the liability of a Sole Proprietor is unlimited.
Q.8. Can I register my Sole Proprietorship Firm at my home or residential address?
Ans: Yes, you can register the company at your residential address.
Q.9. Can I do multiple businesses in one Sole Proprietorship Firm?
Ans: Yes, you can do multiple businesses in one Sole Proprietorship Firm.
Q.10. What isTimelines for Sole Proprietorship Registration?
Ans: The registration process takes approximately 10 days.
For any consultancy in the Formation of proprietorship ||
Contact 7840071184/ 8505999955/ info@ngandassociates.com

