What is a Bonus Issue and How Does it Work?

A bonus issue, also referred to as a bonus share or a capitalization issue, is a corporate action taken by a company to issue additional shares to its existing shareholders at no cost. It is a way for companies to reward their shareholders and capitalize on their accumulated profits or reserves.
When a company declares a bonus issue, it converts a portion of its retained earnings or other reserves into new shares. These new shares are then distributed to the existing shareholders on a pro-rata basis, typically in proportion to their current shareholdings. For example, if a shareholder holds 100 shares and the company declares a 1-for-1 bonus issue, the shareholder will receive an additional 100 shares, effectively doubling their holdings.
The primary purpose of a bonus issue is to increase the number of shares outstanding without diluting the ownership percentage of existing shareholders. While the overall market capitalization of the company remains the same, the number of shares held by each shareholder increases. This can have several potential benefits.
FEATURES OF BONUS ISSUE
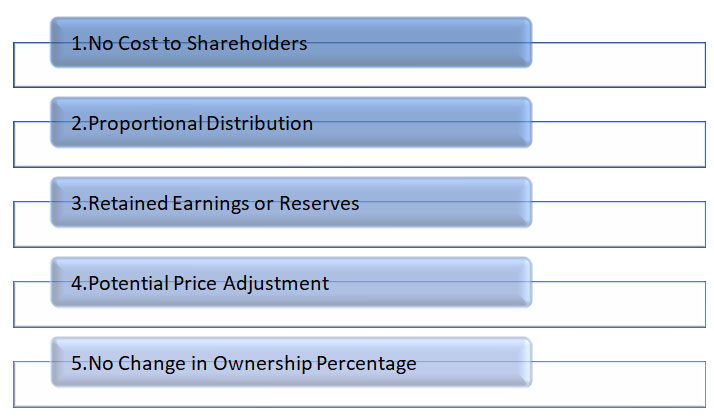
1. No Cost to Shareholders: One of the key features of a bonus issue is that it is offered to existing shareholders at no cost. Shareholders receive additional shares without having to pay any additional money or surrender their existing shares.
2. Proportional Distribution: Bonus shares are typically distributed to existing shareholders on a pro-rata basis. The number of bonus shares allocated to each shareholder is proportionate to their existing shareholding. For example, if a company declares a 1-for-1 bonus issue, shareholders receive one additional share for each share they already own.
3. Retained Earnings or Reserves: Bonus issues are usually funded by a company's accumulated profits or reserves. These can include retained earnings, share premium, capital redemption reserve, or any other available reserves specified by the company's regulations or accounting practices.
4. Potential Price Adjustment: The announcement of a bonus issue can impact the market price of the company's shares. The market price per share may adjust downward to reflect the increased supply of shares in the market. However, the overall market capitalization of the company remains the same.
5. No Change in Ownership Percentage: Despite receiving additional shares through a bonus issue, the ownership percentage of each shareholder remains the same. The proportionate ownership stake of a shareholder in the company remains unchanged as the total number of shares increases.
BENEFITS OF BONUS ISSUE
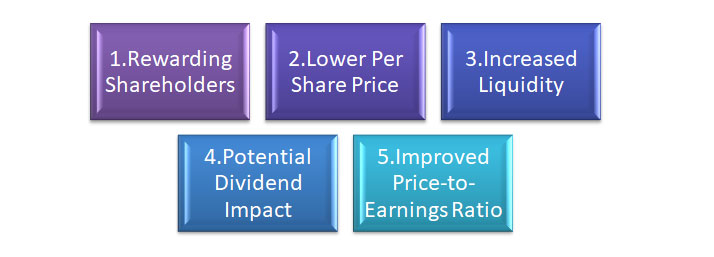
1. Rewarding Shareholders: A bonus issue is a way for companies to reward their existing shareholders. By issuing bonus shares, shareholders receive additional shares without any cost, effectively increasing their ownership stake in the company. This can be seen as a gesture of appreciation and can enhance shareholder loyalty and satisfaction.
2. Lower Per Share Price: The issuance of bonus shares can lead to a decrease in the market price per share. Since the total market capitalization of the company remains the same, the increased number of shares results in a lower price per share. This can make the stock more affordable for new investors and potentially attract a larger investor base.
3. Increased Liquidity: Bonus issues can enhance the liquidity of a company's stock. By increasing the number of shares available for trading, it can attract a broader range of investors and potentially increase trading activity. This increased liquidity can contribute to a more active and efficient market for the company's shares.
4. Potential Dividend Impact: Bonus issues can impact future dividend payments. With the increased number of shares held by each shareholder, the company's earnings can be spread across a greater number of shares. If the company's earnings per share remain stable, shareholders may expect higher dividend payments in the future due to their increased ownership stake.
5. Improved Price-to-Earnings Ratio: A bonus issue can potentially improve a company's price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio. If the bonus issue leads to an increase in the number of shares, while the earnings per share remain stable or increase, the P/E ratio can decrease. A lower P/E ratio may attract investors who consider it an indicator of an undervalued stock.
SOURCES FOR ISSUANCE OF BONUS SHARE
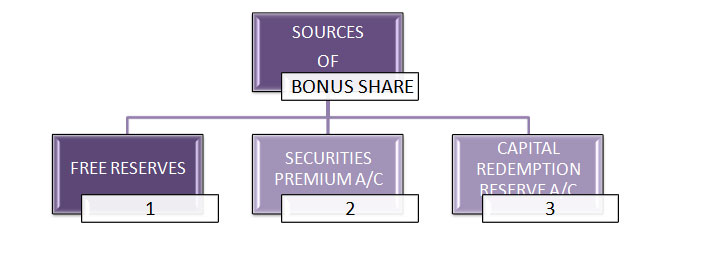
NOTE: No issue of bonus shares shall be made by capitalizing reserves created by the revaluation of Assets.
CHECKLIST FOR ISSUE OF BONUS SHARE
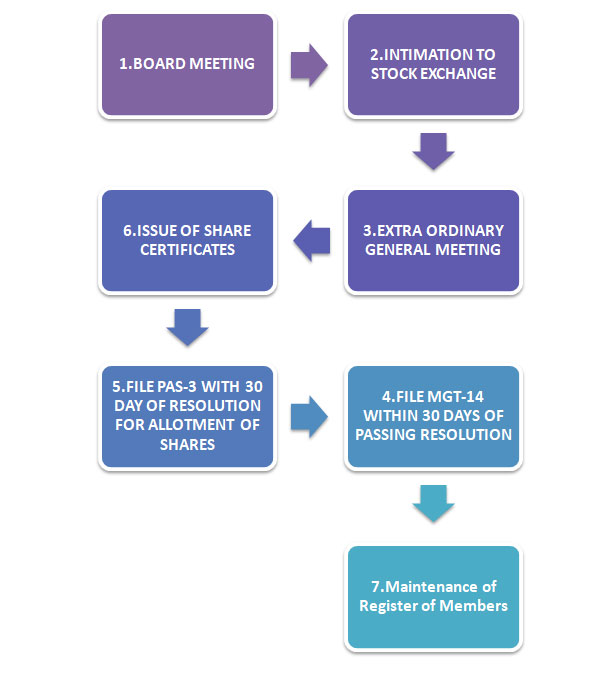
1. Review Articles of Association: Examine the company's Articles of Association to ensure they allow for the issuance of bonus shares. If necessary, seek shareholder approval to amend the articles.
2. Board Resolution: Hold a board meeting and pass a resolution to propose the issuance of bonus shares. The resolution should include details such as the number of shares to be issued and the ratio at which they will be distributed.
3. Shareholder Approval: Convene a general meeting of shareholders and obtain their approval for the bonus share issuance. Follow the legal requirements regarding notice periods and quorum for the meeting.
4. Determine Record Date: Fix a record date to determine the shareholders eligible for receiving the bonus shares. This date is important as only shareholders on record as of this date will be entitled to the bonus shares.
5. Determine Ratio: Decide on the ratio at which the bonus shares will be issued. For example, a 1:1 ratio means one bonus share will be issued for every existing share held.
6. Assess Capitalization: Assess the financial position of the company to determine if it has sufficient reserves or profits to support the issuance of bonus shares. Ensure compliance with any legal requirements related to the capitalization of reserves.
7. Obtain Regulatory Approvals: If required, seek approvals from regulatory authorities such as the Securities and Exchange Commission or stock exchange where the company is listed.
8. Issue Bonus Shares: Once all necessary approvals are obtained, prepare the necessary documents, such as a bonus share issuance notice or letter of allotment, and issue the bonus shares to eligible shareholders.
9. Update Shareholder Records: Maintain accurate records of the issuance, including the names of shareholders receiving bonus shares, the number of shares allotted, and any changes to their shareholding.
10. Stock Exchange Compliance: Comply with any reporting requirements of the relevant stock exchange regarding the issuance of bonus shares, including timely filing of necessary documents and disclosures.
11. Communicate with Shareholders: Inform shareholders about the issuance of bonus shares through appropriate means, such as company announcements or notices.
12. Update Share Certificates: If applicable, issue new share certificates reflecting the bonus shares to shareholders
BASIC PROCEDUE FOR ISSUE OF BONUS SHARE
FAQS
Q.1. What is a bonus issue?
Ans. A bonus issue is when a company distributes additional shares to its existing shareholders without any cost.
Q.2.Why do companies issue bonus shares?
Ans. Companies issue bonus shares as a way to reward existing shareholders and increase the liquidity of their shares in the market.
Q.3. Can a company issue partly paid up Bonus Shares?
Ans. No, Bonus Shares shall always be issued fully paid up.
Q.4. What is the impact of a bonus issue on shareholder value?
Ans. A bonus issue does not change the overall value of the company or the individual shareholder's stake. It merely increases the number of shares held by each shareholder.
Q.5. How are bonus shares allocated?
Ans. Bonus shares are typically allocated to existing shareholders in proportion to their current shareholding.
Q.6. Can bonus shares be sold immediately after they are issued?
Ans. Yes, bonus shares can be sold immediately after they are issued, just like regular shares.
Q.7. Are bonus shares taxable?
Ans. Generally, bonus shares are not taxable when they are issued. However, any future dividends received on bonus shares may be subject to tax.
Q.8. Do bonus shares affect earnings per share (EPS)?
Ans. Bonus shares do not impact the earnings per share (EPS) because the company's earnings are distributed over a larger number of shares.
Q.9. Are bonus issues common?
Ans. Bonus issues are fairly common and are often seen as a way for companies to reward shareholders and enhance their marketability. However, not all companies choose to issue bonus shares.
Q.10. Can company issue Bonus Shares in different ratio to its existing shareholders?
Ans. No, Company cannot issue bonus shares in different ratio, It shall issue bonus shares to the existing shareholders in proportion to their existing holdings.
For any consultancy in the Bonus Issue matter ||
Contact 7840071184/ 8505999955/ info@ngandassociates.com

