The concept of such companies was introduced in Companies Act 1913 that permitted companies with charitable objects etc. to be registered without the words ‘Limited’ or ‘Private Limited’.. Section 25 of Companies Act, 1956 was then introduced for such companies based on English Companies Act 1948. According to the Companies Act 2013, a Section 8 company is defined as an organization whose objectives are to promote arts, commerce, science, research, education, sports, charity, social welfare, religion, environmental protection, or other similar activities goals. It is a non-profit organization (NPO)
- The process of registering a Section 8 Company is same as incorporating an “NGO, Trust, or a Co-operative Society” under the Companies Act 2013.
- An extra necessity must be fulfilled for obtaining a license from the central government under Section 8 of the Companies Act, 2013.
- If the proposed Section 8 Company has been enrolled as a private limited than at least 2 directors are required. But if it is a “public limited Section 8 Company” then a minimum of 3 directors must be there.
- The license, basically, allows them to delete Private/Public Limited from their name. With this permit, the company becomes eligible for the specific exclusions from provisions of law and has concessions in the charge.
As per the rules, if NPO fails to comply with the responsibilities stated by the Central Government, it may lead to winding up of the company on order of the Central Government. Moreover, strict legal actions will be taken against all the members of the company.
• If a company defaults in complying with the provisions of the Act, then it shall, without prejudice to any other action under the provisions of this section, be punishable with a fine which shall not be less than Rs.10 lakhs and may get extend to even Rs.1 crore. The Directors and all other officers of the company, found in default, shall be punishable with imprisonment for a term which may extend to 3-years, or with a fine of not less than Rs.25, 000 that too may extend to Rs. 25 lakhs, or both. Provided that it is proved that the operations were conducted fraudulently.
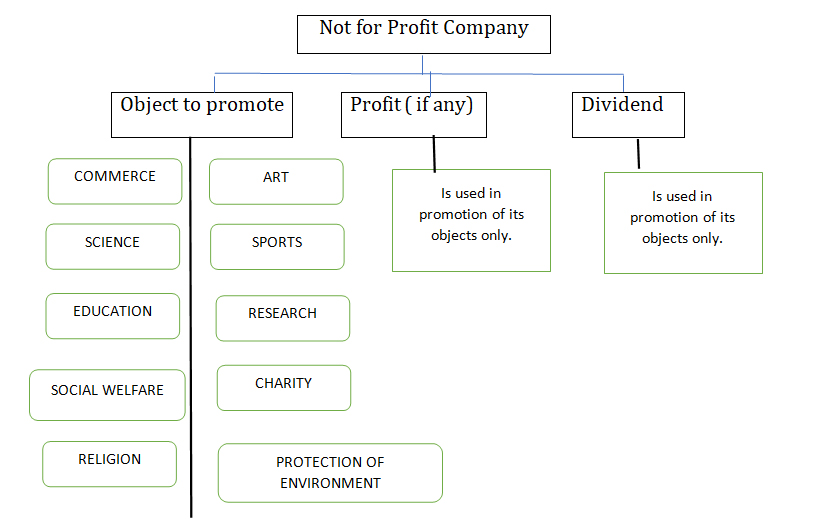
Objective of Section 8 Company
Primary objective of section 8 company is to work for the welfare of the society in the fields of science, art, sports, education, research, environment protection etc.
Such company intends to apply its profit in promoting its objects and prohibiting the payment of any dividend to its members.
OBLIGATIONS OF SECTION 8 COMPANIES
- There should be a clear vision and project plan of the company for the next 3 years
- Directors or promoters of the company cannot withdraw any remuneration in any form.
- The entire profit of the company which is generated must be used towards the furtherance of their cause and meeting the objectives
- No dividend should be paid to any of their members or directors of the company either directly or indirectly.
- Section 8 Company shall include the words like – Foundation, forum, association,federation, chamber, confederation, Council, electoral trust and like etc.
- In case of revocation, the company may get wind-up. Or it may be simply asked to change its name by adding either “Private Limited or Public Limited”.
- And the assets remaining after clearing debts and liabilities of such a Company shall be transferred to some other Section 8 Company having similar objects.
- Then every officer in default shall be liable for action.
- Any such order shall not be passed unless the company has been given a reasonable opportunity of being heard.
Registration Process for Section 8 Companies
To incorporate a Section 8 Company, an application shall be made to the Registrar of Companies in Form no. INC.12, which shall be accompanied, inter alia, by the following documents:
a. Prepare DSC and file name approval.
b. Minimum two directors and two members are required to incorporate it.
c. Draft Memorandum of Association (MOA) and Articles of association (AOA) of the Company in prescribed format (Form no. INC – 13) where the photographs of subscribers are affixed
d. A Declaration is to be attached in Form no. INC-14 (on the stamp paper, duly notarized) by an Advocate, a Chartered Accountant, Cost Accountant or Company Secretary in practice, that the draft memorandum and articles of association have been drawn up in conformity with the provisions of section 8 and rules made there under and all the requirements under section 8 have been complied with.
e. An estimate of the future annual income and expenditure of the company for next three years, specifying the sources of the income and the objects of the expenditure.
f. A declaration (in Form no. INC-15) on stamp paper duly notarized by each of the persons making the application and
g. Form no. INC-9 from each subscribers and first directors, on appropriate stamp paper of the State and duly notarized.
The Central government has also brought out certain exemptions to Section 8
Companies under Section 462 of Companies Act 2013.
1. Notice : Section 8 Company can hold a meeting with minimum 14 days notice as against 21 days notice.
2. Minutes: Section 118 (Minutes) does not apply as a whole except that minutes may be recorded within 30 days of the conclusion of the meeting in case of companies where the articles of association provide for confirmation of minutes by circulation.
3. Independent director : Section 8 Companies are exempted from the requirement of appointment of independent director and all the consequential provisions relating to Independent directors under section 149(1) of the Companies Act.
4. Company Secretary: Appointing a Company secretary is not mandatory for section 8 companies Incentives
5. No. of Directors: Directors of the company can obtain positions in more than 20 companies.
6. No minimum capital : There is no minimum share capital requirement in section 8 company incorporation.
7. Tax Benefit: The income of section 8 company is completely tax free if the company has obtained 80G and 12A registration.
8. Caro: Requirements of Companies Auditor’s Report Order or CARO do not apply to this type of company.
9. Financial Statements: copy of audited financial statements shall be sent to various recipients not less than 14 days before the date of meeting to stakeholders
Annual Compliances for Section 8 companies as per the Companies Act 2013
- Conduction of minimum of two board meetings in a year.
- Maintenance of Books of Accounts
- Preparation of Financial Statements
- Mandatory Audit
- Income tax return filing
- Filing of financial statements in form AOC 4
- An annual return is to be filed every year with other e- filing forms like MGT 7.
- Additional compliances to fulfil the registration like 12AA, 80G etc
DOCUMENTS REQUIRED
For Directors/Shareholders
- Copy of PAN Card
- Aadhaar Card
- Address Proof (Bank Statement, Electricity Bill, Telephone Bill)
- 2 Passport Sized Photographs
For Registered Office
- Ownership Proof (House Tax etc.)
- Utility Bill (Electricity Bill, Gas Bill)
- Address Proof (Bank Statement, Electricity Bill, Telephone Bill)
Important Points
Minimum Requirement:
- A Section 8 Company gets incorporated by the MCA.
- All requirements of the Companies Act 2013, such as the minimum number of Directors and Shareholders, etc. must be met with
Charitable Object
- Section 8 Companies can be established for non-profit objectives only. Any profit earned or income received by this Company is not to be distributed among its members.
- This implies that the income will either be reinvested in the business or utilized for the progress of its main objects, i.e. charitable purpose.
Management Team
- Unlike other Trusts which are governed by the Trustees as per a Trust Deed, the operations of Section 8 Companies are managed by the Board of the Directors as per their “MoA and AoA”.
Companies Act, 2013
A “Section 8 Company” must follow the provisions prescribed under the Companies Act, 2013, such as “Maintaining Book of Accounts, Audits, Return Filing, Board Meetings, etc”.
MoA&AoA
A Section 8 Company shall not make any changes to the provisions of it’s “MoA&AoA” without seeking approval from the Central Government first.
Voting Rights
The voting rights of the shareholders of a Section 8 Company are based on the number of shares held by them. Similar to that of any other company.
Income tax
The Company has to follow the provisions of the Income Tax Act.
GST Registration
If Section 8 Company comes under the purview of the GST Act, it must get registered with GST.
Conversion
It may not convert itself to any other kind of company structure without complying with conditions, as applicable.
Donations/Funding of Section 8 Company
Section 8 Company is not allowed to raise capitals by way of deposits but they can accept donations from the general public. Below are some of the ways by which it can raise funding:
- Foreign Donations: Foreign donations are allowed only when FCRA (Foreign Contribution Regulation Act, 1976) registration has been taken. FCRA license can only be applied after 3-years from the date of registration. However, if some really urgent foreign donations are necessary, then you may apply for prior permission from the commissioner.
- Equity Funding: A “Section 8 Company” can also raise funds by issuing new equity shares at a higher value.
- Domestic donations: There is no limitation to domestic donations. But to avoid money laundering cases, a proper system must be laid down to keep them in check.
Conclusion
If the operations of the Company are found to be conducted fraudulently or in violation of the objects of the Company or unfavorable to public interest then, also, the license can be revoked.
The objective of the section 8 company cannot be altered without prior permission of the Central Government of India.
FAQ
What is a Section 8 company?
It is a type of not-for-profit company set up for the promotion of art, science, commerce, charity, sports, education, research, or any other useful activity. These companies are typically formed to benefit a specific community or purpose and are excluded from the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013 that generally apply to other companies.
2. Can Section 8 company make profit? Yes, Section 8 companies can make a profit. Section 8 companies are businesses that receive subsidies from the government to provide services to low-income people. They can also use different ways to gain incomes such as - Investment, Donations, Funding, etc.
3. How long it will take to incorporate a Company?
The time taken for registration will depend on the submission of relevant documents by the client and the speed of Government Approvals. To ensure speedy registration, please choose a unique name for your Company and ensure you have all the required documents prior to starting the registration process.
4. What is difference between NGO and Section 8 company?
A Non-Governmental Organization (NGO) is an organization that is independently established and operated, usually with a charitable, educational, religious, or social purpose. NGOs are usually non-profit and do not have a profit motive.
A Section 8 Company is a non-profit organization formed to promote commerce, art, science, sports, education, research, social welfare, religion, charity, protection of environment or any other such object. Section 8 companies are allowed to generate profit but they must use their profits for the purpose of achieving their goals and not for the benefit of its members.
5.How long is the registration of the Company valid?
Once a Company is incorporated, it will be active and in existence as long as the annual compliances are met with regularly. In case, annual compliances are not complied with, the Company will become a Dormant Company and may be struck off from the register after a period of time. A struck-off Company can be revived for a period of up to 20 years.
6. Can Section 8 company make profit?
Yes, Section 8 companies can make a profit. Section 8 companies are businesses that receive subsidies from the government to provide services to low-income people. They can also use different ways to gain incomes such as - Investment, Donations, Funding, etc.
7. Do I have to be present in-person to incorporate a Section 8 Company?
No, you will not have to be present at our office or appear at any office for the registration of a Section 8 Company. All the documents can be scanned and sent through email to our office. Some documents will also have to be couriered to our office.
8. What are the documents required for registration?
Identity proof and address proof are mandatory for all the proposed Directors of the Section 8 Company. PAN Card is mandatory for Indian Nationals. In addition, the landlord of the registered office premises must provide a No Objection Certificate for having the registered office in his/her premises and must submit his/her identity proof and address proof.
9. What is a Digital Signature Certificate?
A Digital Signature establishes the identity of the sender or signee electronically while filing documents through the Internet. The Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) mandates that the Directors sign some of the application documents using their Digital Signature. Hence, a Digital Signature is required for all Directors of a proposed Section 8 Company
10. What is the Director Identification Number?
Director Identification Number is a unique identification number assigned to all existing and proposed Directors of a Company. It is mandatory for all present or proposed Directors to have a Director Identification Number. Director Identification Number never expires and a person can have only one Director Identification Number.
11. Can NRIs /Foreign Nationals be a Director in a Section 8 Company?
Yes, a NRI or Foreign National can be a Director in a Section 8 Company after obtaining Director Identification Number. However, at least one Director on the Board of Directors must be a Resident India.
12. Is an office required for starting a Section 8 Company ?
An address in India where the registered office of the Company will be situated is required. The premises can be commercial/industrial/residential where communication from the MCA will be received.
For any consultancy in the incorporation of Section 8 company ||
Contact 7840071184/ 8505999955/ info@ngandassociates.com

